(The Conversation) South Africans had to deal with the worst ever series of power cuts in 2022. All told, the country lost a record 205 days of electricity due to constant breakdowns at the coal-fired power plants run by Eskom, the state-owned electricity utility. The plants are old and have not been sufficiently maintained.
The country’s energy crisis has been escalating since April 2008, when scheduled power cuts were first implemented.
One of the biggest casualties of more than a decade of severe power outages has been the country’s water processing and distribution networks. The most recent, and escalated, blackouts have led to water utilities in parts of the country issuing warnings about damage to water supply infrastructure and operations.
The negative effects on water supply are far-reaching. Energy and water are intertwined. The water reticulation system – the transport of water from source, the treatment of water and sewage, and the distribution and delivery of water to consumers – all require electricity.
A number of cities, including Johannesburg and Nelson Mandela Bay, as well as smaller towns, have had drastic water cuts.
These experiences – as well as the growing frequency of sewage spills – have given South Africans a glimpse of what the future might hold if the energy crisis is not properly addressed. Water shortages and prolonged cuts in supply are likely to become increasingly common.
How it works
A typical piped water supply system consists of the following:
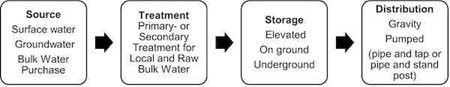
Water Reticulation System.
Water processing and distribution networks require electricity to pump water, for example, to water towers and reservoirs, and then to consumers. Prolonged power cuts halt this process if no suitable back-up pumps are in place.
The same applies to water treatment plants. Prolonged power outages can cause sewage spills if no working back-up pumps are in place.
The problems triggered by the power cuts have been made worse by the fact that the country’s water infrastructure has been deteriorating for decades. Water losses have been increasing as a result of decaying infrastructure such as old pipes.
The country also suffers from unsustainable water demand – there is not enough water available to meet increasing demand from various sectors and consumers. Continued water pollution also decreases the amount of water that is fit for use or consumption, contributing to water stress.
Allegations of corruption and misappropriation of funds have also plagued the sector.
What are the potential solutions?
Water utilities have recognized the increase in water disruptions and outages.
Consumers have been urged to:
- use less water during prolonged outages to decrease the risk of limiting water supply. Decreasing water consumption assists municipalities in dealing with operational challenges such as water towers and reservoirs reaching critically low levels.
- ensure they have water to last through the power outage (4 hours or more).
Other steps taken:
- Water restrictions have been imposed to decrease consumption, for example, in the City of Johannesburg.
- The City of Johannesburg is establishing contracts to lease mobile generators, specifically for prolonged power outages.
- The National Energy Crisis Committee, a body run out of the president’s office, has proposed various measures such as importing energy from neighbouring countries, buying excess energy from private producers, and developing emergency legislation to speed approval and development of power plants.
https://techxplore.com/news/2023-01-power-south-africa-playing-havoc.html


